Eye Floaters and Retinal Detachment: Understanding the Warning Signs
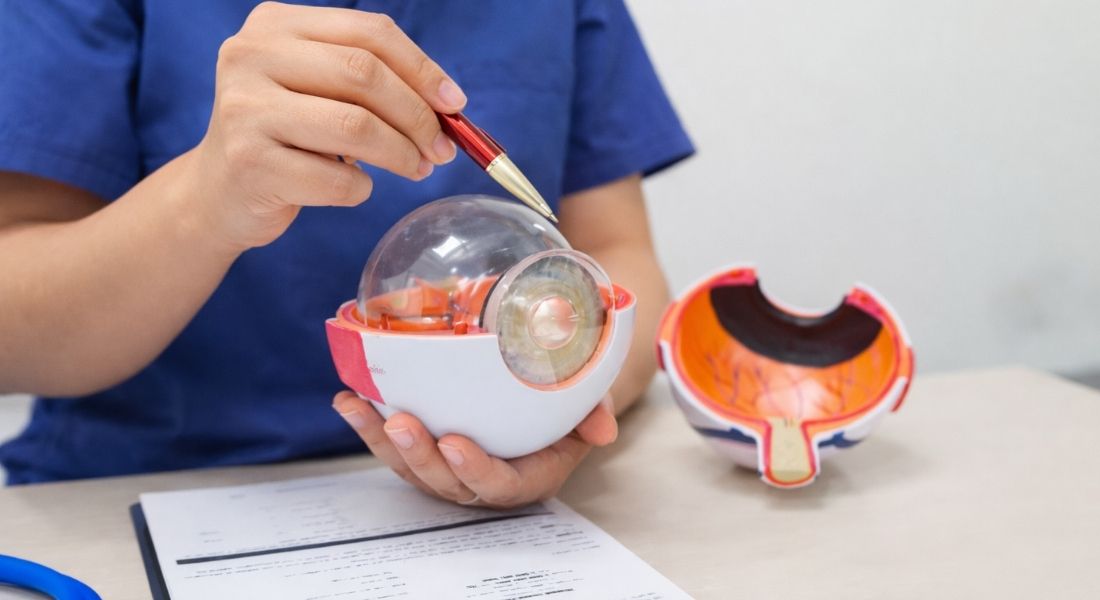
If you notice eye floaters in your vision, you may be wondering whether they are just a normal part of aging or something more serious. While most floaters are harmless and common, they can sometimes indicate a sight-threatening condition like retinal detachment. Understanding how to tell the difference between benign floaters and the type linked to retinal detachment is essential for your eye health.
Retinal detachment is a serious condition where the retina, which is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye, pulls away from its normal position. If not treated urgently, it can lead to permanent vision loss. Recognising the warning signs early can make a significant difference in the outcome, which is why it is important to know when to seek urgent care.
In this article, we explain how retinal detachment-related floaters differ from benign floaters. We’ll also discuss the symptoms that should raise red flags, and why seeking immediate professional assessment is essential. Understanding these key points can help protect your vision and prevent serious complications.
What Are Eye Floaters?
Eye floaters are small shapes or spots that appear in your vision, usually when you look at a bright, plain background, like a clear sky or a white wall. They often look like squiggly lines, cobwebs, or little specks, and they tend to move as you move your eyes. Floaters are a common occurrence and generally become more frequent as we age.
Floaters form when the vitreous gel inside the eye begins to break down or shrink. This process creates tiny clumps of cells or debris that cast shadows on the retina, which is why you see them. While floaters can be annoying, they are usually harmless and do not pose a risk to your vision.
In most cases, floaters are not a cause for concern. However, when they occur suddenly or in combination with other symptoms, they may be indicative of a more serious problem, such as retinal detachment. Understanding the differences is key to protecting your eye health.
How Retinal Detachment Relates to Eye Floaters
Retinal detachment occurs when the retina becomes separated from the underlying tissue, disrupting its ability to send visual signals to the brain. This can be triggered by a tear or hole in the retina, often associated with sudden changes in the vitreous gel. When this happens, floaters may appear suddenly, and they may be more pronounced or persistent.
Unlike the benign floaters most people experience, those linked to retinal detachment can be much more noticeable. You may see an increase in the number of floaters or notice a sudden onset of dark, shadowy areas in your peripheral vision. These changes can occur rapidly and should not be ignored.
If you experience a sudden increase in floaters, flashes of light, or a shadow or curtain moving across your field of vision, it may indicate retinal detachment. These are serious warning signs that require immediate assessment by an eye care professional.
Red Flag Symptoms of Retinal Detachment
When eye floaters occur alongside certain visual changes, they can signal a serious problem with your retina. Retinal detachment happens when the retina begins to separate from the tissue that supports it, and this can lead to permanent vision loss if not treated quickly. Being able to recognise the warning signs helps you seek help before lasting damage occurs.
- Sudden or dramatic increase in floaters: If you notice a sudden surge in floaters, particularly if they appear as a dense cluster of spots, strands, or cobweb-like shapes, this may indicate that the retina is being torn or pulled. This change often feels very different from the occasional floaters you may already be used to and should always prompt urgent assessment.
- Flashes of light in your peripheral vision: Flashes can look like brief flickers, lightning streaks, or shimmering lights, usually noticed at the edges of your vision. These occur when the vitreous gel tugs on the retina, causing it to become irritated or stretched. Frequent or persistent flashes are an important warning sign that should not be ignored.
- A shadow, veil, or curtain spreading across your vision: One of the clearest signs of retinal detachment is a dark shadow or curtain-like effect moving across your field of vision. This often starts in the periphery and gradually spreads towards the centre, reducing your ability to see clearly. Any form of sudden vision loss, even if partial, is a medical emergency.
These symptoms are not something to “wait and see.” If you experience any combination of these warning signs, you should seek urgent medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis and prompt treatment greatly improve the chances of preserving your sight and preventing permanent vision loss.
Why Immediate Assessment is Essential
Retinal detachment is a medical emergency. The sooner treatment is provided, the better the chance of saving vision. Without prompt intervention, retinal detachment can lead to permanent blindness in the affected eye.
The urgency of seeking professional care cannot be overstated. If caught early, retinal detachment can often be treated with laser surgery or a surgical procedure to reattach the retina. Delaying treatment may result in the need for more invasive procedures, and in some cases, it may not be possible to save vision.
If you notice any symptoms associated with retinal detachment, it is crucial to contact an eye care professional immediately. Quick assessment and action are the key to protecting your vision.
What Happens During a Retinal Detachment Evaluation?
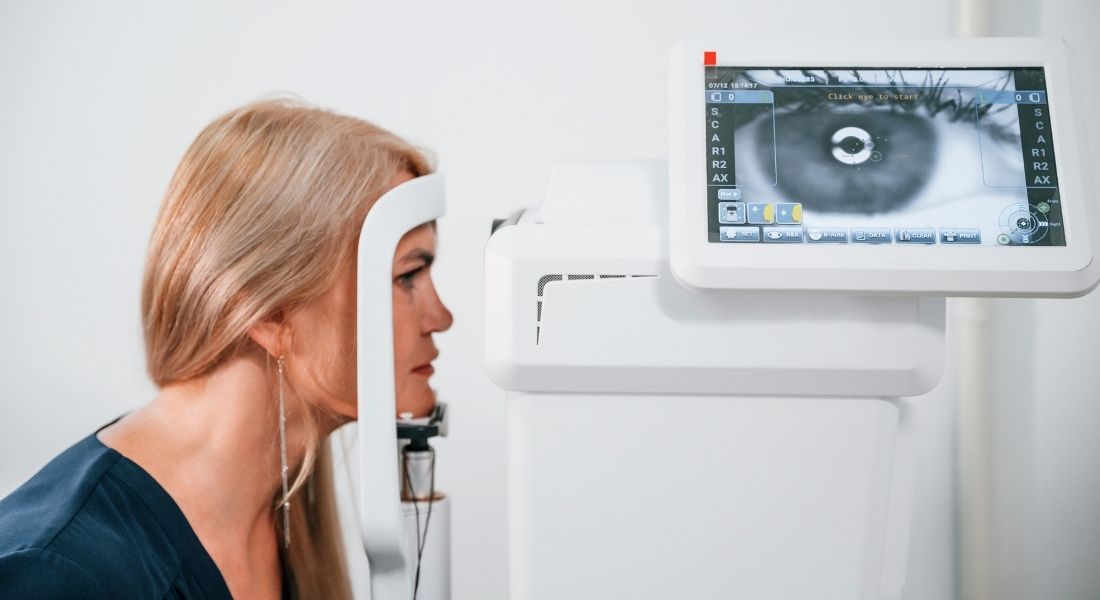
When you visit an eye care professional for a retinal detachment assessment, the first step is a thorough eye exam. This usually involves dilation of the pupils to allow the doctor to fully examine the retina. Depending on your symptoms, the doctor may also perform additional imaging tests such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) or a fundus photography to capture detailed images of your retina.
If a retinal tear or detachment is found, the doctor will discuss your treatment options with you. The goal of treatment is to repair the tear or reattach the retina as soon as possible. Depending on the severity of the detachment, options may include laser surgery, cryopexy (freezing treatment), or a vitrectomy (removal of vitreous gel).
Treatment is often effective when performed early. Your doctor will discuss the best course of action based on your specific situation and health condition.
Can Floaters Be Treated?
While most floaters are harmless, treatment may be recommended if they significantly interfere with your vision. Laser treatment can sometimes be used to break up the floaters, making them less noticeable. However, this procedure is typically reserved for cases where floaters are particularly bothersome or associated with more severe conditions like retinal tears.
In some cases, if the floaters are a symptom of a larger issue like retinal detachment, the primary treatment will focus on addressing the underlying cause. Once the root issue is treated, the floaters may naturally decrease in frequency or severity.
If your floaters are benign and not causing significant disruption, they usually do not require intervention. Regular monitoring by your eye care provider ensures that any changes in your eye health are addressed promptly.
Why Some People Experience More Floaters Than Others
As you age, the vitreous gel in your eye naturally changes. These changes often cause floaters to appear more frequently. However, some people may be more prone to floaters due to other factors such as myopia (nearsightedness), eye injuries, or a family history of retinal problems.
While most floaters are harmless, they can be annoying. If you have a higher risk due to one of these factors, it is important to have regular eye exams to monitor any changes in your eye health. Early detection of any retinal issues increases the likelihood of successful treatment.
Your eye care provider can guide you on the best ways to manage and monitor floaters, ensuring that they don’t interfere with your quality of life.
LASIK Surgery and Floaters: What to Expect

If you are considering LASIK surgery and have floaters, it’s important to discuss this with your eye surgeon. LASIK involves reshaping the cornea, but it does not directly affect the vitreous gel or floaters. However, the suction applied during the procedure may cause temporary discomfort or exacerbate any existing floaters.
In most cases, LASIK surgery is safe for patients with floaters. The procedure addresses vision correction rather than floaters themselves. If floaters are a concern, your surgeon can provide advice on how to manage them during your recovery period.
Floaters do not usually impact the effectiveness of LASIK surgery, but they can be a temporary inconvenience. If they are particularly bothersome, your eye care provider will discuss possible solutions before proceeding with LASIK.
When to Seek Urgent Help for Eye Floaters
While most eye floaters are harmless, some changes should never be ignored. If floaters appear suddenly or are accompanied by other visual symptoms, you should seek urgent medical attention. Acting quickly can make a critical difference in protecting your sight.
You should seek immediate eye care if you notice any of the following alongside your floaters:
- A sudden increase in the number of floaters: If you notice a rapid appearance of many new floaters, especially if they look like dark spots, strands, or a cloud of debris, this may indicate a retinal tear. This change is often very noticeable and different from the occasional floaters you may already be used to.
- Flashes of light in your vision: Flashes can appear as brief streaks, flickers, or lightning-like arcs, usually at the edges of your vision. These flashes may be more noticeable in dim lighting or when you move your eyes, and they can occur when the vitreous pulls on the retina.
- A shadow, veil, or curtain moving across your vision: A dark shadow or curtain-like effect spreading across your peripheral vision is one of the most serious warning signs. This symptom may gradually move towards the centre of your vision and can indicate an active retinal detachment.
- Sudden blurring or loss of part of your vision: Any rapid change in vision clarity or loss of vision in one area should be treated as urgent. Even partial vision loss requires immediate assessment.
These symptoms can be caused by a retinal tear or retinal detachment, both of which are medical emergencies. Delaying assessment increases the risk of permanent vision loss. If you experience any of these warning signs, do not wait to see if they settle seek urgent eye care straight away to give yourself the best chance of preserving your sight.
Frequently Asked Questions:
- Are eye floaters always a sign of retinal detachment?
No, eye floaters are very common and are often a normal part of ageing. In most cases, they are caused by natural changes in the vitreous gel inside the eye and are harmless. However, a sudden increase in floaters or floaters combined with other symptoms may indicate a more serious issue such as a retinal tear or detachment. - How can I tell the difference between normal floaters and dangerous ones?
Normal floaters tend to develop gradually and remain fairly stable over time. Dangerous floaters usually appear suddenly, increase rapidly in number, or occur alongside flashes of light or changes in vision. Any noticeable change that feels different from your usual experience should be assessed promptly. - Do flashes of light always mean retinal detachment?
Flashes of light do not always mean retinal detachment, but they are an important warning sign. They often occur when the vitreous gel pulls on the retina, which can sometimes lead to a tear. If flashes are frequent, persistent, or accompanied by floaters, urgent eye examination is essential. - Can retinal detachment happen without pain?
Yes, retinal detachment is typically painless. This is why it can be dangerous, as people may delay seeking help if they are not experiencing discomfort. Visual changes such as floaters, flashes, or shadows are usually the only warning signs. - How quickly should I seek help if I notice sudden floaters?
You should seek urgent eye care as soon as possible, ideally on the same day. Retinal conditions can progress quickly, and early treatment significantly improves the chances of preserving vision. Waiting even a short time can increase the risk of permanent damage. - Can retinal detachment be cured if caught early?
If detected early, retinal detachment can often be successfully treated. Procedures such as laser treatment or surgery can reattach the retina and prevent further vision loss. While vision may not always return to normal, early intervention offers the best possible outcome. - Are certain people more at risk of retinal detachment?
Yes, people who are very short-sighted, have had previous eye surgery, experienced eye trauma, or have a family history of retinal problems are at higher risk. Ageing also increases risk due to natural changes in the vitreous gel. - Can stress or screen use cause eye floaters?
Stress and screen use do not directly cause floaters, but eye strain can make existing floaters more noticeable. Floaters are caused by physical changes inside the eye rather than lifestyle factors. However, regular eye examinations are still important if visual symptoms worsen. - Will eye floaters ever go away on their own?
In many cases, floaters become less noticeable over time as the brain learns to ignore them or as they settle within the eye. While they may not disappear completely, most people find that floaters become less bothersome without treatment. - Should I get my eyes checked even if my floaters seem mild?
Yes, especially if the floaters are new or changing. Even mild symptoms can sometimes indicate early retinal issues. A professional eye examination provides reassurance and ensures that any serious conditions are detected early.
Final Thought: Protecting Your Vision from Floaters and Retinal Risks
Eye floaters are often harmless, but when they appear suddenly or alongside symptoms such as flashes of light or changes in vision, they should never be ignored. Understanding the warning signs of retinal detachment and knowing when to seek urgent care can make a critical difference in protecting your eyesight. Acting quickly allows problems to be identified early, when treatment is most effective and the risk of permanent vision loss is lower.
If your floaters are persistent, worsening, or affecting your quality of life, a professional assessment can provide clarity and reassurance. If you’re exploring whether specialist floaters treatment in London could benefit you, get in touch with us at Eye Clinic London to schedule your consultation and ensure your eye health is properly looked after.
References:
- Sebag, J., Vitreous floaters, Ophthalmology, 90(11), discusses how changes in the vitreous gel contribute to floaters and the high prevalence of posterior vitreous detachment in symptomatic patients, underlining the clinical relevance of floaters as a symptom. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S016164208334392X
- Olsen, T.W. & Jeppesen, P., Symptoms related to posterior vitreous detachment and the risk of developing retinal tears: a systematic review, Acta Ophthalmologica, reports that floaters and flashes significantly increase the risk of retinal tears and detachment, supporting the need for prompt examination when symptoms arise. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30632695/
- Evaluation and Management of Retinal Detachment. In: Retinal Detachment: Principles and Practice. Oxford Academic. https://academic.oup.com/book/41818/chapter-abstract/354570267
- Ahmed, F. and Tripathy, K. (2023). Posterior vitreous detachment, StatPearls, NCBI Bookshelf. This review describes posterior vitreous detachment as the most common cause of symptomatic floaters and explains that sudden onset of floaters and flashes can signal retinal tears requiring urgent medical care. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563273/
- Olsen, T.W. and Jeppesen, P. (2019). Symptoms related to posterior vitreous detachment and the risk of developing retinal tears: a systematic review, Acta Ophthalmologica Scandinavica, examines how the onset of flashes and floaters especially when both are present are associated with a higher risk of retinal tears and subsequent retinal detachment, underscoring the need for immediate evaluation. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30632695/

